Variables and Datatypes
11:01 AM
Posted by Sai Subramanyam
Variable and its Scope
There are mainly 2 types of variables in Java.They are: Instance variables and Member Variables(Class variables).
Instance Variables are the variables which are created while instantiating a class.
Class variables are the normal variables which are declared casually inside a class.
Note : The static variables also come under class variables.
Datatypes Explained
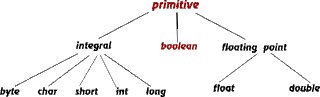
In the previous section we came across the various datatypes and its categories.Lets have a deep look at them.
- Integer Datatypes(int,byte,short,long) are used to store signed integers values.The memory size of the datatypes of byte,short,int,long are 1,2,4,8 respectively.
Note : A long literal is generally ended with ' L '.Ex: 32L.
- Floating Point Datatypes(float,double) are used to store the decimal type(fractional type) values.The memory size of the datatypes of float,double are 4,8 bytes respectively.The floating point literals float must end with ' f '.And double literal must take a precission of two places or else there will be a Loss In Precesion Error by compiler.
Example : 2.8f - float literal.
2.85 - double literal.
- Character Datatype(char) are used to store single Unicode characters.The memory size is 2 bytes.
- Boolean Datatypes are used to store the values which are either true or false .
Video tutorial:
So,we covered the Language basics till here and from next parts we will go into the more serious parts which are useful in coding.
Stay Tuned for more posts!!
Au Revoir!!
This entry was posted on October 4, 2009 at 12:14 pm, and is filed under
Java Basics
. Follow any responses to this post through RSS. You can leave a response, or trackback from your own site.
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Post a Comment